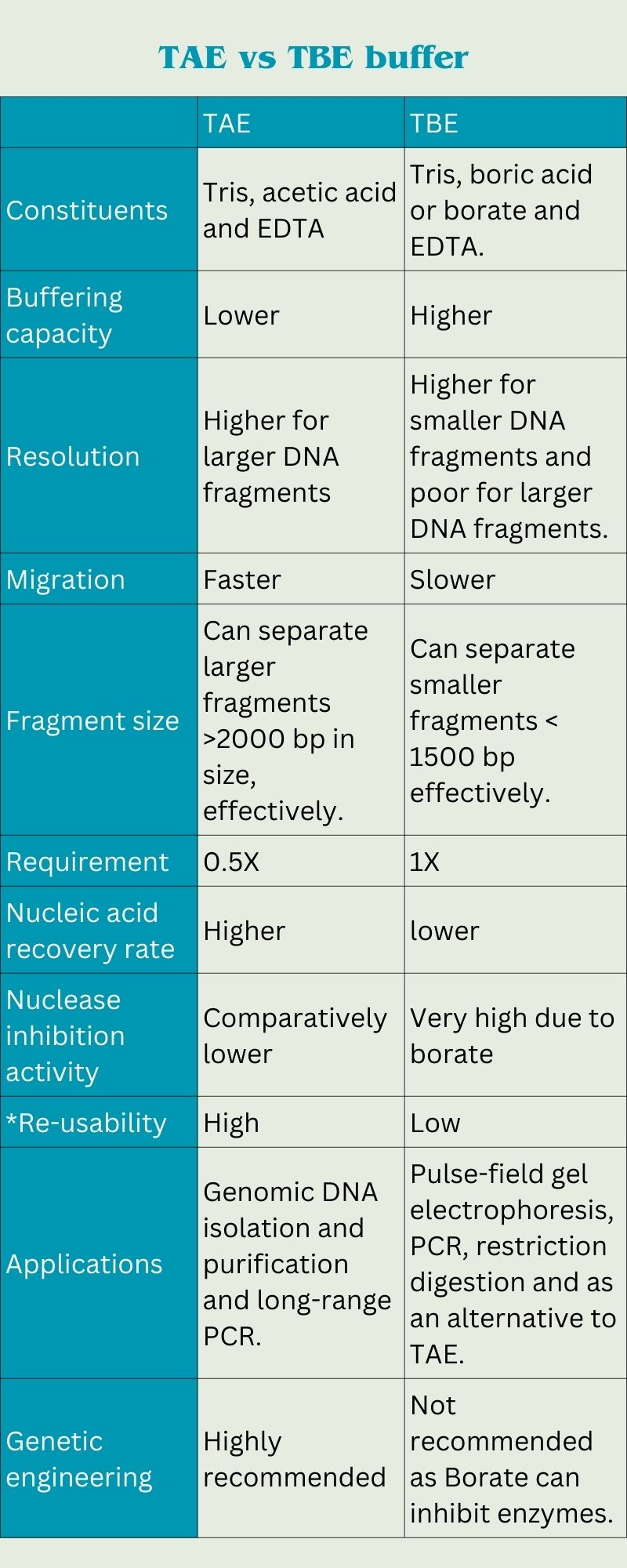
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a vital technique used in molecular biology for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. This method relies on the properties of agarose gel and specific running buffers to achieve precise results. Among the buffers used, TAE (Tris-Acetate-EDTA) and TBE (Tris-Borate-EDTA) are the two most commonly utilized. Each buffer has its unique characteristics that affect the resolution and migration of nucleic acids during electrophoresis. In this post, we will explore the applications of these buffers and provide a visual representation of the agarose gel electrophoresis process.
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Buffer
The choice of buffer can significantly influence the results of your electrophoresis. TAE buffer is often preferred for applications involving larger DNA fragments, while TBE is typically used for smaller fragments, providing better resolution. Below is an illustration detailing the agarose gel electrophoresis process:
 Ingredients for Agarose Gel Preparation
Ingredients for Agarose Gel Preparation
- 1x TAE or TBE buffer
- 0.8 to 2% agarose powder (depending on the size of DNA fragments being separated)
- DNA sample (for analysis)
- Loading dye (to track DNA migration)
- Ethidium bromide or an alternative gel stain (for visualization under UV light)
Instructions for Preparing Agarose Gel
- Begin by measuring your agarose powder. Depending on your specific requirements, 0.8% to 2% concentration is typical.
- Combine the agarose powder with the desired buffer (TAE or TBE) in a heat-resistant flask.
- Heat the mixture in a microwave or hot plate until the agarose is completely dissolved, being careful to avoid boiling over.
- Allow the solution to cool to about 50-60°C before adding any ethidium bromide or staining solution.
- Pour the cooled agarose solution into a gel caster with a comb in place and let it set for approximately 30-60 minutes at room temperature.
- Once the gel has solidified, carefully remove the comb and place the gel into the electrophoresis chamber, ensuring it is submerged in the running buffer.
- Load your DNA samples mixed with loading dye into the wells created by the comb, and connect the electrophoresis unit to a power source to begin the separation process.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between TAE and TBE buffers, as well as proper gel preparation techniques, is essential for achieving successful results in DNA analysis. Utilizing the correct methods plays a crucial role in the field of molecular biology research and diagnostics.
Handy 10X TBE Buffer Recipes for Experiments
 source = geneticeducation.co.in
source = geneticeducation.co.in